Atmospheric plasma and low pressure plasma are the two primary categories that industrial plasma systems would fit into.
Atmospheric plasma and low pressure plasma are the two primary categories that industrial plasma systems would fit into.
The industrial atmospheric plasma system is designed to ionize a stream of flowing gas and treat a material surface through exposure to the stream of partially ionized gas .

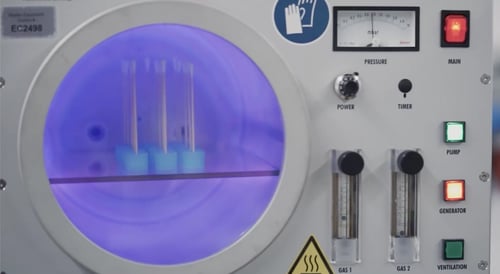
Low pressure plasma requires putting the parts in a vacuum chamber of partially ionized gas to get the surface to be treated in contact with the plasma. The low pressure plasma system pumps the gas out of the vacuum chamber and replacing the gas with a process gas at a controlled pressure. This gas is then excited to a plasma state as fresh feed gas is introduced as the vacuum pump continuously removes gas from the process chamber to maintain the process pressure.
To remove the parts from the vacuum chamber the process gas and power to sustain the plasma reaction are discontinued. The chamber is flushed with gas to remove any gas residue that would cause unfavorable industrial hygiene or be harmful to the operator. The vacuum pump is then isolated from the vacuum chamber. Then gas(usually air) is added to the chamber to equalize the pressure in the chamber to room pressure allowing the chamber to be opened and the treated parts removed.
Parts are processed continuously, process is performed at room pressure, clean dry compressed air is often the process gas, systems are reliable and have good operational equipment efficiency, tooling can be integrated to a robot for production automation,
Entire part treated during processing, low takt times easily achievable on large surface area parts, able to achieve high surface energy in materials atmospheric plasma can not, able to provide ultra-clean surface chemistry over other methods, works well with corrosive service gases, provides operator isolation from process chemistry
Small area of process during treatment, large volume of gas required to process ( ~cubic meter per hour), takt time for large parts is high, compatible process gases limited, limited process gas selection, requires ventilation of working area
Parts processed in a batch, parts processed in a vacuum chamber
To learn more about the use of plasma in manufacturing, please read our eBook titled "Manufacturer’s Surface Activation Guide for Improved Adhesion."