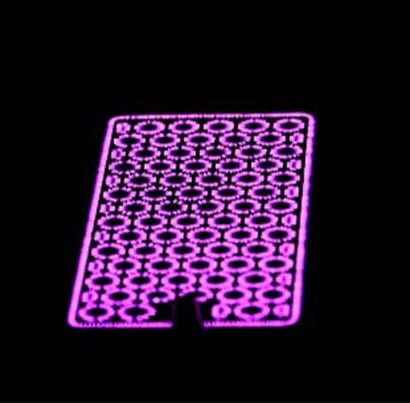
A dielectric barrier discharge is a dry method of plasma treatment which doesn't generate waste water or require drying of the material after treatment.
Plasma is produced by two electrodes with a dielectric between these electrodes to limit the current flow in the plasma. This low density plasma can be described as Dielectric Barrier Discharge or DBD for short.
This method of plasma production is also called silent discharge due the current limiting dielectric controlling the rate of ionization of the gas. This relatively low density plasma produces controlled ionization of the available gas generating little to no detectable sound. This method of low level density plasma production is useful in gas plasma processing like ozone generation, gas reforming, and broad area low level activation processes.
To generate a DBD plasma, high-frequency voltage is applied across one or more insulating layers in the current path between the metal electrodes in addition to the discharge space. This method of plasma generation can be configured planar like the image below or cylindrical in configuration. As a result below, a plasma is generated in the holes of the ceramic.
The ceramic plate can be designed to customer requirements.
One of the key principles of using DBD to generate a plasma is that the plasma can be produced at atmospheric pressure and other pressures. This means that you can generate plasma and expose a gas to molecular dissociation without pumping it down inside a vacuum chamber. This molecular dissociation in combination with catalization events leads to gas reforming efficiencies difficult to perform by other methods.
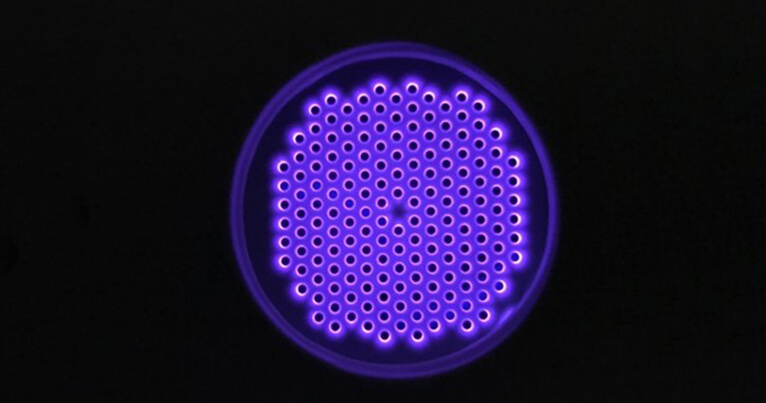
Another use of Dielectric Barrier Discharge is the process of gas scrubbing for emissions or control of greenhouse gas generation. The ability to dissociate the molecular structure of a gas and recombine it to limit specific molecular emission or optimize a molecular generation can be possible with Dielectric Barrier Discharge application to gas.
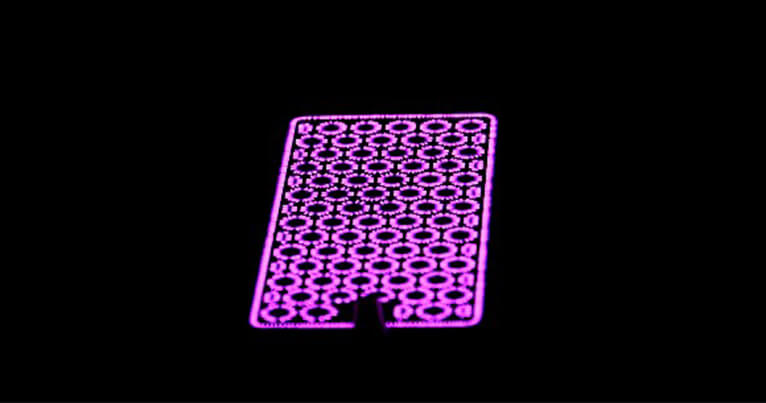
Molecular dissociation of a gas used in combination with different catalyzing methods can be one of the steps used in the process of fuel generation by molecular reconfiguration of a gas.
Another use of Dielectric Barrier Discharge is the process of gas scrubbing for emissions or control of greenhouse gas generation. The ability to dissociate the molecular structure of a gas and recombine it to limit specific molecular emission or optimize a molecular generation can be possible with Dielectric Barrier Discharge application to gas.
Activation of an endless fabric, film, or foil can be passed along the proximity of a Dielectric Barrier Discharge. In this way, a very large surface is activated using the ozone generated. For this reason, it is important to use an extraction system with prolonged operation of DBD in closed spaces for good industrial hygiene.

Control Cabinet:
W 562 mm H 211 mm D 450 mm
Generator:
1 pc. with 40 kHz
Control:
Semi-Automatic

Control Cabinet:
W 562 mm H 211 mm D 450 mm
Generator:
1 pc. with 40 kHz
Control:
PC

Control Cabinet:
W 562 mm H 360 mm D 650 mm
Generator:
1 pc. with 40 kHz
Control:
PC